A chromophil is a cell which is easily stainable by absorbing chromium salts used in histology to increase the visual contrast of samples for microscopy.
Function
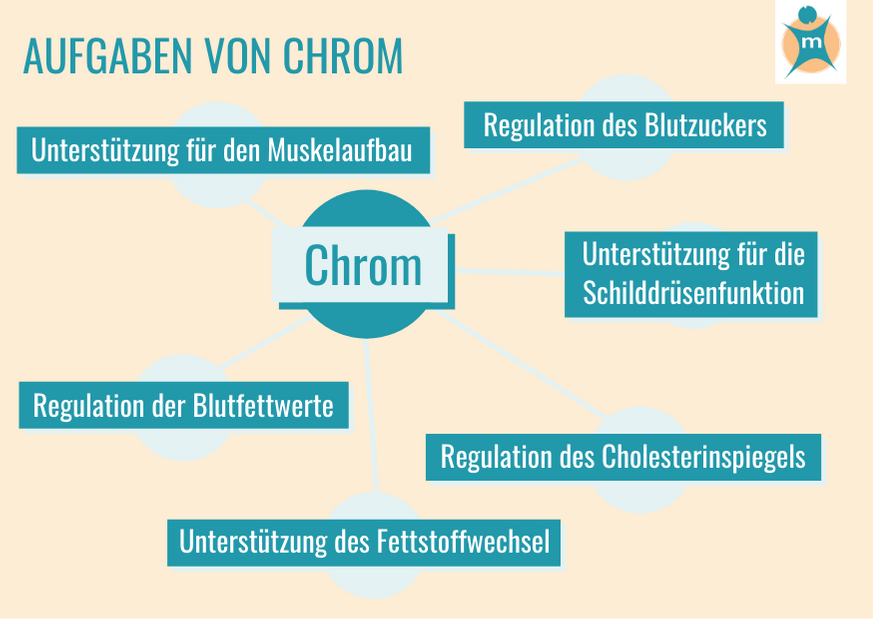
Chromophil cells are mostly hormone-producing cells containing so-called chromaffin granules. In these subcellular structures, amino acid precursors to certain hormones are accumulated and subsequently decarboxylated to the corresponding amines, for example epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine or serotonin. Chromophil cells therefore belong to the group of APUD (amine precursor uptake and decarboxylation) cells.
Location
These cells are scattered throughout the whole body, but particularly in glands such as the hypothalamus, hypophysis, thyroid, parathyroid and pancreas. In adult animals, chromophil cells make up the largest portion of the stria in the cochlear duct.
See also
- Chromophobe cell
- Melanotroph
- Acidophil cell
- Basophil cell
- Oxyphil cell (pathology)
- Oxyphil cell (parathyroid)
- Pituitary gland
- Neuroendocrine cell
References